
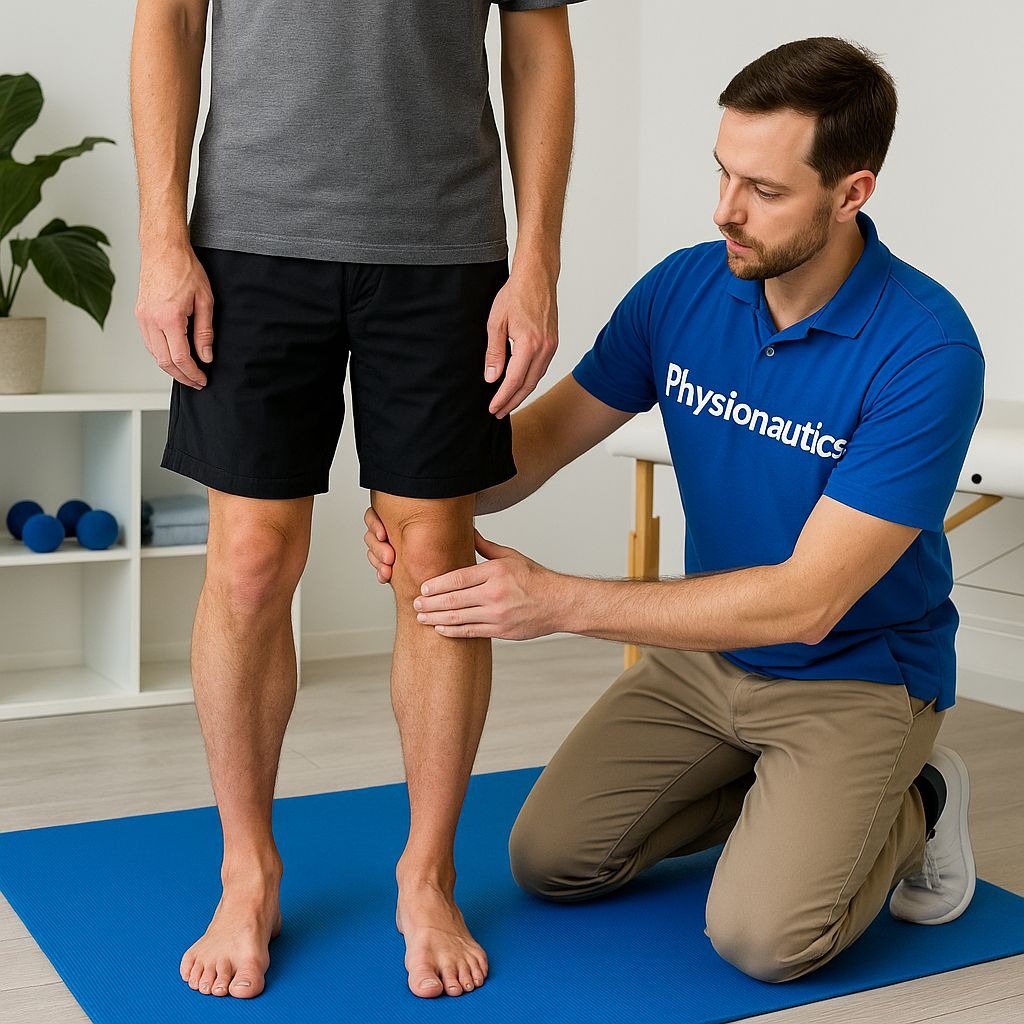
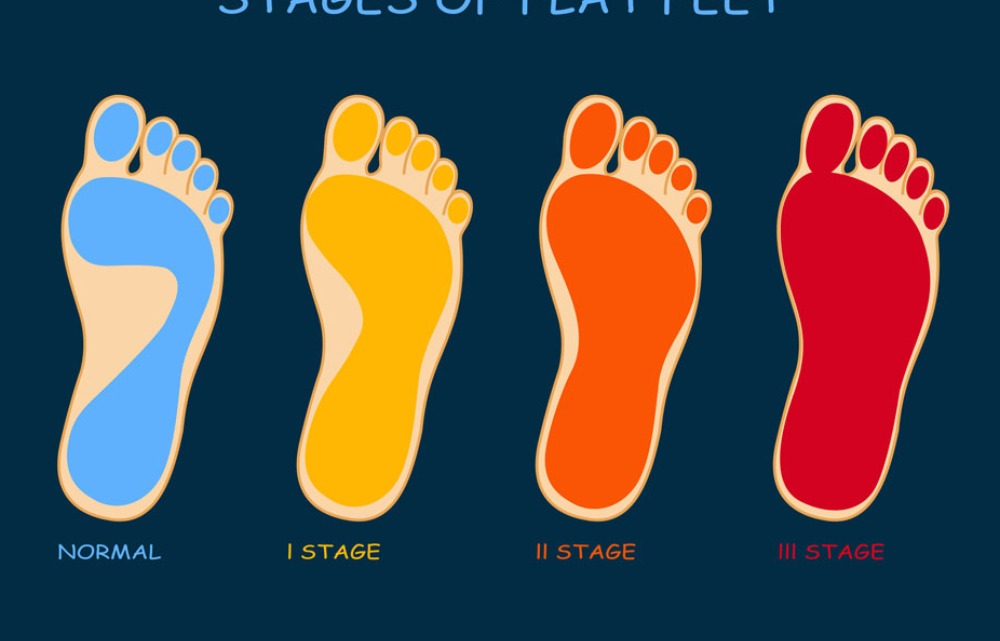

BEST PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR PES PLANUS Flat feet, also known as pes planus, is a condition characterized by the collapse of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot, causing the entire sole to make contact with the ground when standing or walking . This condition can range from flexible, where the arch is present when non-weight-bearing, to rigid, where the arch is absent regardless of weight-bearing . Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing pes planus, aiming to alleviate pain, improve foot flexibility, strengthen weak muscles, and enhance proprioceptioN. Clinical Presentation The causes of flat feet can be varied. Some individuals are born with flat feet (congenital), while others develop them later in life (acquired) . Congenital flat feet can be due to genetic factors or underlying conditions present at birth, such as cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, or certain connective tissue disorders . Acquired flat feet can result from conditions like posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, Charcot foot (related to diabetes), arthritis, or injuries to the foot ligaments . Obesity, foot and ankle injuries, and ligamentous laxity can also contribute to the development of flat feet .Physiotherapy Management The clinical presentation of pes planus can include foot pain, especially after activity, inward-turned ankles, and difficulty walking . Other symptoms may include stiffness in the arches, edema on the medial side of the foot, and contracture of the foot and ankle muscles on the lateral side . Pain Management Physiotherapy is a key component in the management of pes planus, focusing on pain management, flexibility training, strengthening exercises, and proprioception exercises . Flexibility Training Pain management techniques include rest, activity modification, cryotherapy, heat therapy, soft tissue massage, and combination therapy (ultrasound and pulsed electrical stimulation) . These methods aim to reduce discomfort and promote healing . Strengthening Exercises Flexibility training involves passive range of motion exercises for the ankle and foot joints, stretching of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, and Achilles tendon stretching . Heel stretches and tennis/golf ball rolls can also be incorporated to improve flexibility . Proprioception Exercises Strengthening exercises are crucial to prevent valgus and flattening of the anterior arch . These exercises target muscles such as the anterior and posterior tibialis, flexor hallucis longus, intrinsic foot muscles, and abductor hallucis. Specific exercises include arch muscle strengthening with theraband, single-leg weight-bearing, toe walking, eccentric gastrocnemius strengthening, squatting with proper foot alignment, arch lifts, calf raises, stair arch raises, towel curls, and toe raises . Lifestyle Modifications Specialized techniques and manual therapies, such as kinesio taping, ankle joint mobilization and manipulation, and static or dynamic cupping therapy, may also be used . Specialized Techniques and Manual Therapies Proprioception exercises, performed on surfaces like foam, rocker boards, or Bosu balls, help improve balance and coordination .These exercises include toe and heel walking, single-leg weight-bearing, toe clawing of towels and pebbles, forefoot standing on a stair, and toe extension and fanning/spreading . Role of Physical Therapy Lifestyle modifications, such as footwear modifications (wearing shoes with proper arch support and cushioning) and the use of orthotics or braces, can also be beneficial . Weight loss through exercise and dieting may also help . Physiotherapy for pes planus focuses on a comprehensive approach that includes pain management, flexibility exercises, strengthening exercises, proprioception training, and lifestyle modifications to improve foot function and reduce symptoms. Physical therapists are movement experts who can assess, diagnose, and treat flat feet in children and adults . They develop individualized treatment programs based on the patient's condition and goals . These programs may include patient education, manual therapy, balance and gait training, muscle strengthening and stretching, and orthotics . Physical therapists also coordinate with other specialists, such as orthotists or podiatrists, when necessary .
We hate spam too.