
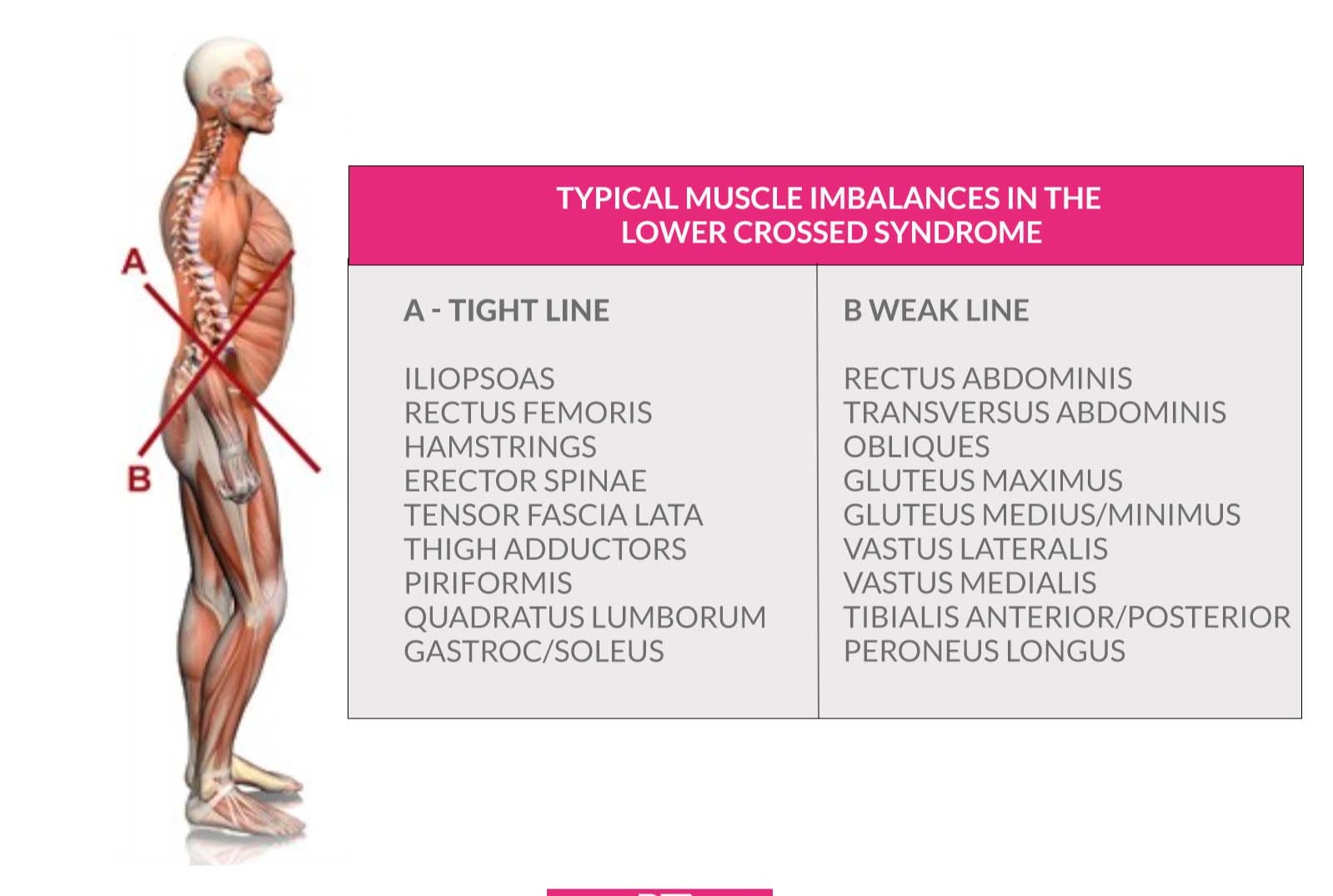

BEST PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR LOWER CROSS SYNDROME Lower cross syndrome, also known as pelvic crossed syndrome, occurs if there is inadequate muscle strength, leading to an imbalance in the lower extremities. This condition is characterized by the weakening and tightening of muscle groups on the anterior and posterior aspects of the CAUSES:The most common cause of LCS is a sedentary lifestyle. Sitting for prolonged periods can cause an imbalance between the muscles to develop. Another potential cause is overtraining certain parts of the body while undertraining others. SYMTOMS: Back Pain Due to the increased lumbar curve and overactive back muscles. Hip Pain: From the tight hip flexors and compensatory movement patterns. Pelvic Tilt: Often noticeable as an anterior tilt, causing postural imbalances. Reduced Mobility: Difficulty in bending, lifting, and other movements involving the hips and lower back. Altered Gait: Walking, running, bending, standing, sitting are all affected by strength and mobility imbalances in the lower body. Muscle Stiffness: Particularly in the lower back and hip flexors. TREATMENT : Physical therapy is a cornerstone of LCS treatment, focusing on retraining the muscle groups responsible for the imbalance. Specific exercises include 1. Relaxing the Muscles: This can be achieved using a foam roller to address tender spots in muscles like the quads and inner thighs. 2. Lengthening and Static Stretching: Holding static stretches for 30 seconds, such as the iliopsoas stretch, is beneficial. 3. Activating and Strengthening the Muscles: Exercises with little or no external resistance are performed, holding positions for a few seconds and performing multiple repetitions. Examples include bridges and hip extensions. 4. Integrating Movement Patterns: Following the physical therapist's advice on integrated movement patterns helps the brain understand how to move the muscles correctly. Additional Treatment Options -Ergonomic Setup: If working from home, invest in an ergonomic work setup, including a desk of suitable height and a supportive chair. Movement Breaks: Set reminders to get up and move or stretch regularly. Prioritize Exercise: Schedule physical activity into your day.Proper Posture: Practice good posture and frequently move underactive muscles. Hydration: Drink water often to encourage more frequent movement. The most effective treatments aim to fix the imbalance by strengthening some muscles and stretching or relaxing others. Acupuncture and Dry Needling: These can help relieve pain and reduce muscle tension. Myofascial release therapy: it can help relax tight muscles and improve blood flow. Chiropractic Care: Adjustments to correct postural imbalances.
We hate spam too.