
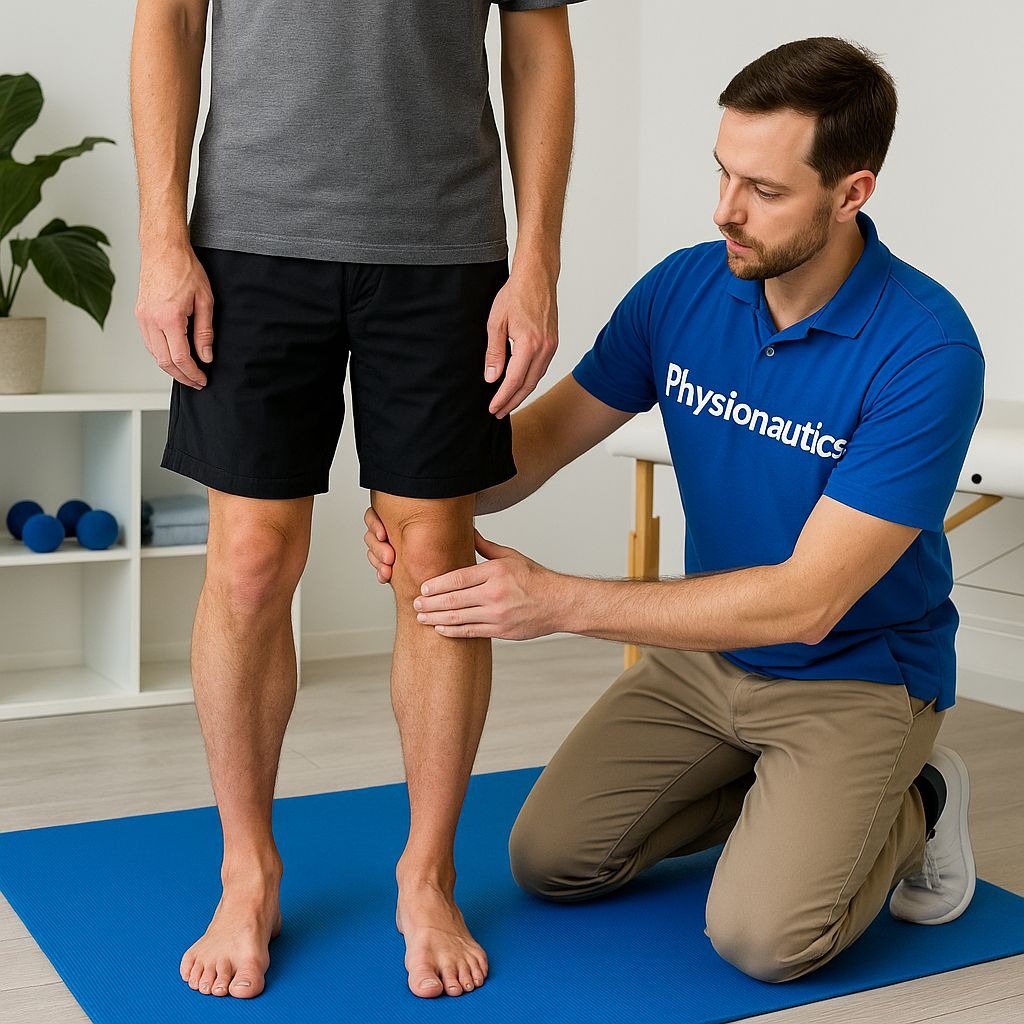

AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF HIP /OSTEONECROSIS Avascular necrosis is the death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply. Also called osteonecrosis, it can lead to tiny breaks in the bone and cause the bone to collapse.. CAUSES: Traumatic Causes: Fractures: Fractures of the femoral neck or head can damage the blood vessels supplying the femoral head, leading to AVN. Dislocations: Dislocation of the hip joint can also disrupt blood flow to the femoral head. Non-Traumatic Causes: Corticosteroid Use: Long-term or high-dose use of corticosteroids, Alcohol Abuse, Coagulopathies: Other Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, osteoporosis, and HIV can also increase the risk of AVN, Radiation Therapy, Gaucher's Disease, Idiopathic: In some cases, the cause of AVN is unknown. SYMPTOMS:In the early stages of this bone disorder, you may not display any symptoms. But as AVN progresses, you may have: Mild to moderate hip or groin pain. Pain while walking or when moving the hip. You may also have pain that radiates down to the knee.Stiffness in the hip joint. Trouble putting weight on one leg, often causing you to limp. At first, the pain may get better with rest. But, in the later stages of AVN, the pain can be more constant. Treatment;Treatment consists of supportive therapy and pain management Treatment includes physiotherapy, surgery and medication.SurgeryBone surgery, Arthroplasty and Bone graftingMedications, :Nonsteroidalanti-inflammatory drugSelf-care:Quit smoking and Limit alcohol intake Therapies:Physical TherapyWeight-bearing restriction: Using crutches or other gait aids reduces stress on the joint, allowing the bone time to heal. Manual therapy: Gentle mobilizations help maintain range of motion and encourage blood flow to the area. Strengthening exercises: Focus on hip and thigh muscles to protect the joint and improve stability. Gentle exercises: Improve circulation and promote healing. Modalities: Heat, electrical stimulation, or pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) may be used to enhance blood flow and bone growth. Advanced Stages: Focus on regaining range of motion After a hip replacement, physiotherapy helps to restore movement and strength. Strengthening program: Emphasizes the core and back muscles, which play a crucial role in hip stability. Endurance and coordination training: Walking on a treadmill or cycling may be used to improve fitness and co ordination
We hate spam too.